The National Library of France Turns the Page With a Monumental Refresh From the Design Atelier of Bruno Gaudin Architectes
Among the many palaces of Paris, France, a country steeped in grand, elaborate constructions, the Bibliothèque Nationale de France on the rue de Richelieu is one for the books. A Beaux-Arts beauty by architect Henri Labrouste, this cathedral of French culture is the now the grand dame of a contemporary age, courtesy of a Herculean overhaul from Paris-based practice Bruno Gaudin Architectes.
One might assume that in the face of the city’s more lionized architectural prizes—the Eiffel Tower, the Arc de Triomphe, Versailles—that the National Library of France might not merit much notice. But with all those decorative theatrics, this c’est magnifique set piece leaves no confusion as to where one might be. This is France.

And this, the National Library of France, is history, with tentacles tracing back to imperial times when a royal library was founded at the Louvre Palace, housed in a succession of sites, then pried from aristocratic hands during the French Revolution. The collection expanded, with a big assist coming from Napoleon’s conquests, and the library became public in the 1600s.
It went on to survive calamity, including two world wars, as well as a series of scattershot repairs in the 1950s. By the time Bruno Gaudin was tasked with reviving the library’s block-long Richelieu site, the literary institution was woefully unsuitable for contemporary use. Renovating the structure would take 15 years and two phrases to complete, but in the end, the library had, as the practice puts it, taken “possession of a new, large and luminous stone vessel.”
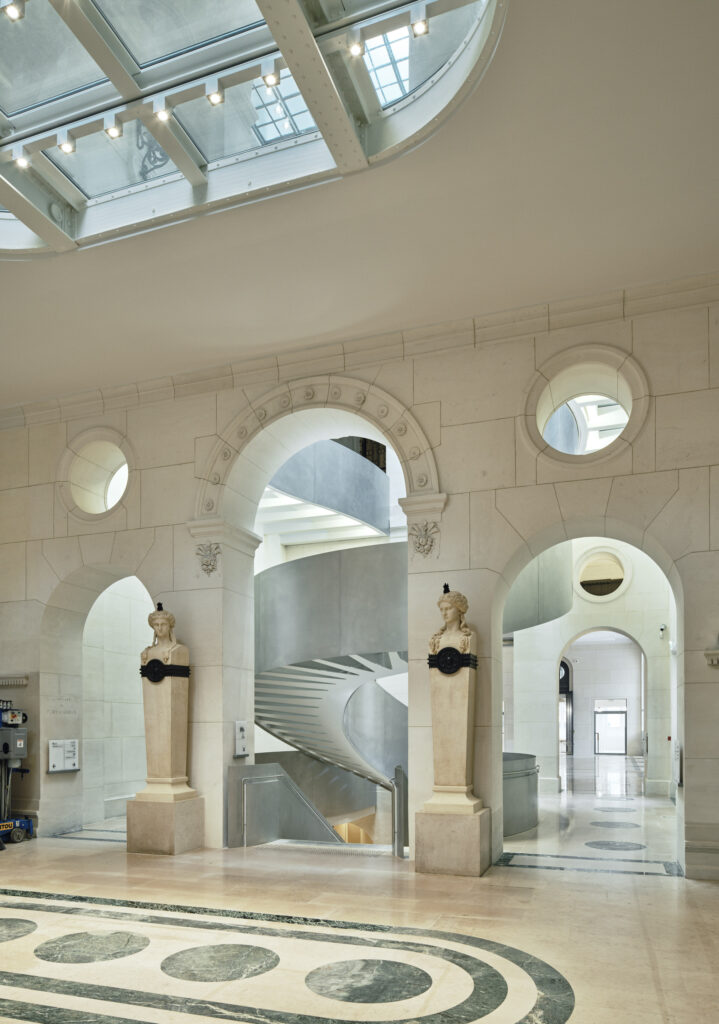

At the start of the process, in 2007, the practice had in its possession a labyrinth. Confronted with a “vast tangle” of spaces built over three centuries, the building was a cramped, slow creep of accumulation from “constant transformations, enlargements, demolitions and densifications.”
Just like a great book can drift outside the margins, revealing something unexplored, the architects discovered behind the library’s well-ordered stone facades “hidden buildings that had been redesigned or even rebuilt many times, sometimes with up to 14 floors. This long history of library construction, often led by great architects,” they note, “offers…a building of a complexity commensurate with the rich heritage of the spaces that characterize it.”
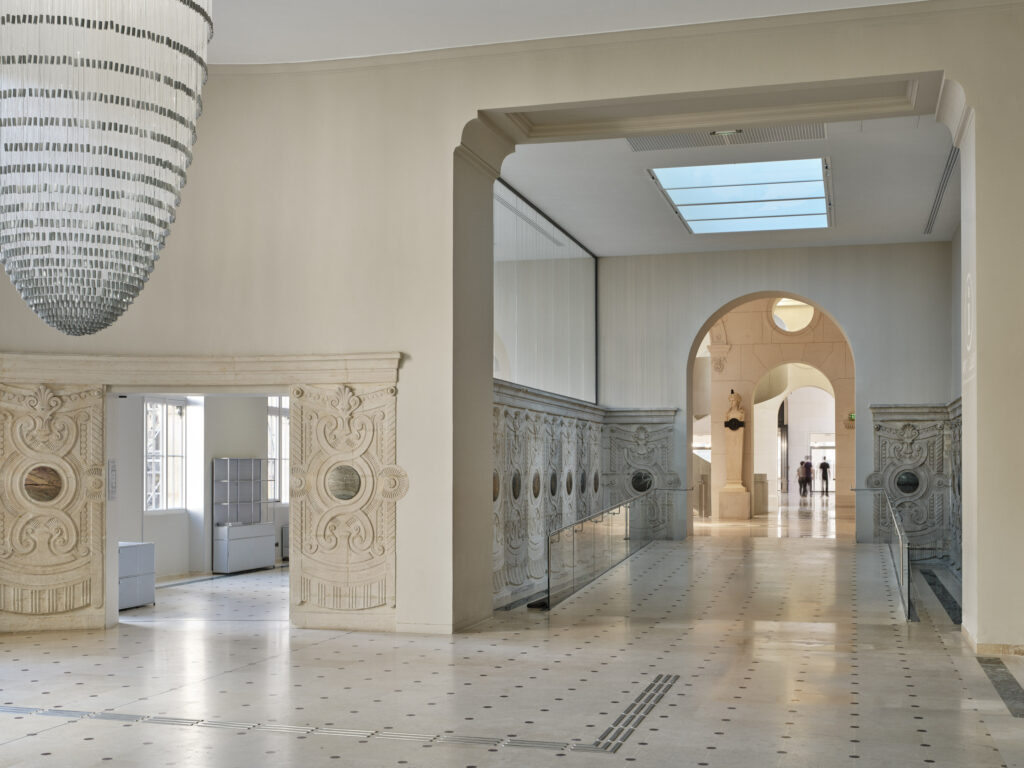

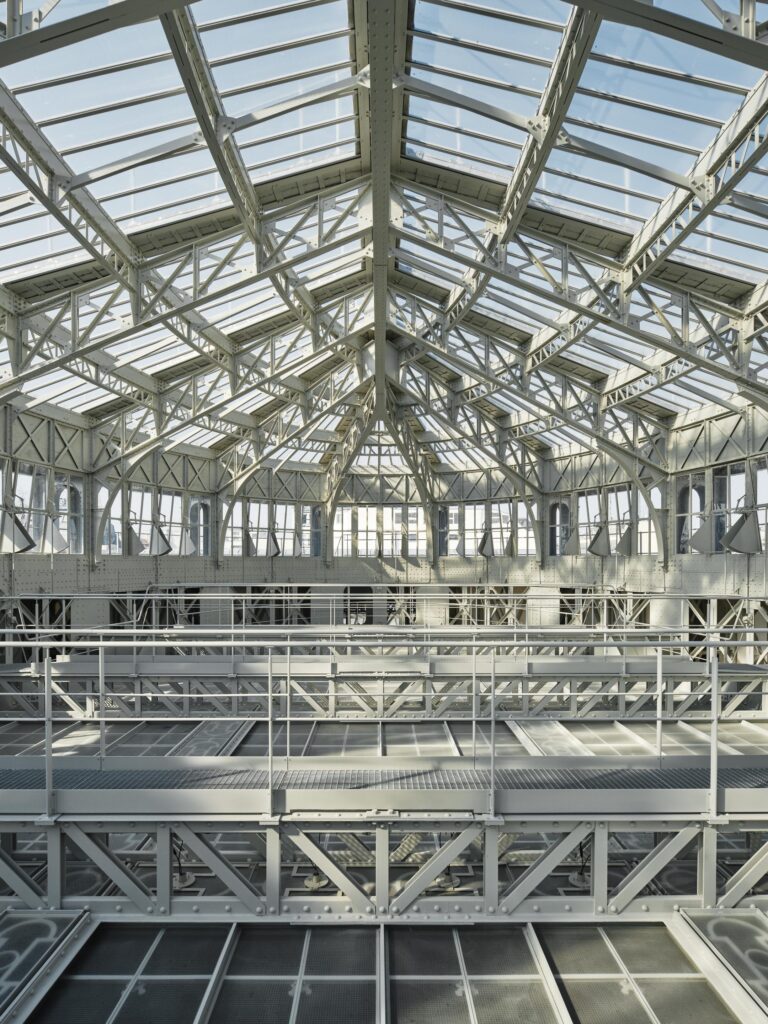
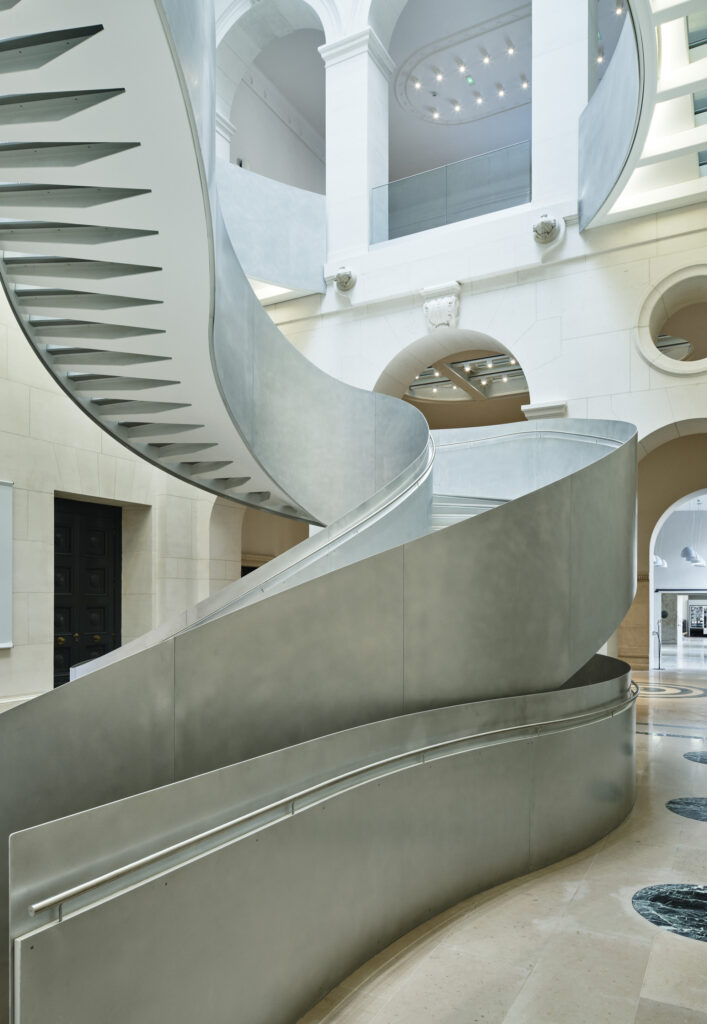
Complexity brings challenge and, in this case at least, profound transformation. The architects reconfigured circulation for the library to open and give it light. They introduced a new entrance and courtyard, and, in a pivotal move, switched out staircases, trading in the old main staircase for a shiny aluminum-clad statement.
“In architecture, the staircase is an object of choice,” the practice observes. “Its space, form and place say a lot about the way it has been designed and thought out.” Here that idea translated in a stupendous metallic spiral that lends aesthetic tension to an antique canvas that had become stodgy without something fresh. One would not dare classify the new staircase in simple utilitarian terms as “a fire safety necessity” that “can be punished in a dark corner of the plan, caged, disappearing from our view.”
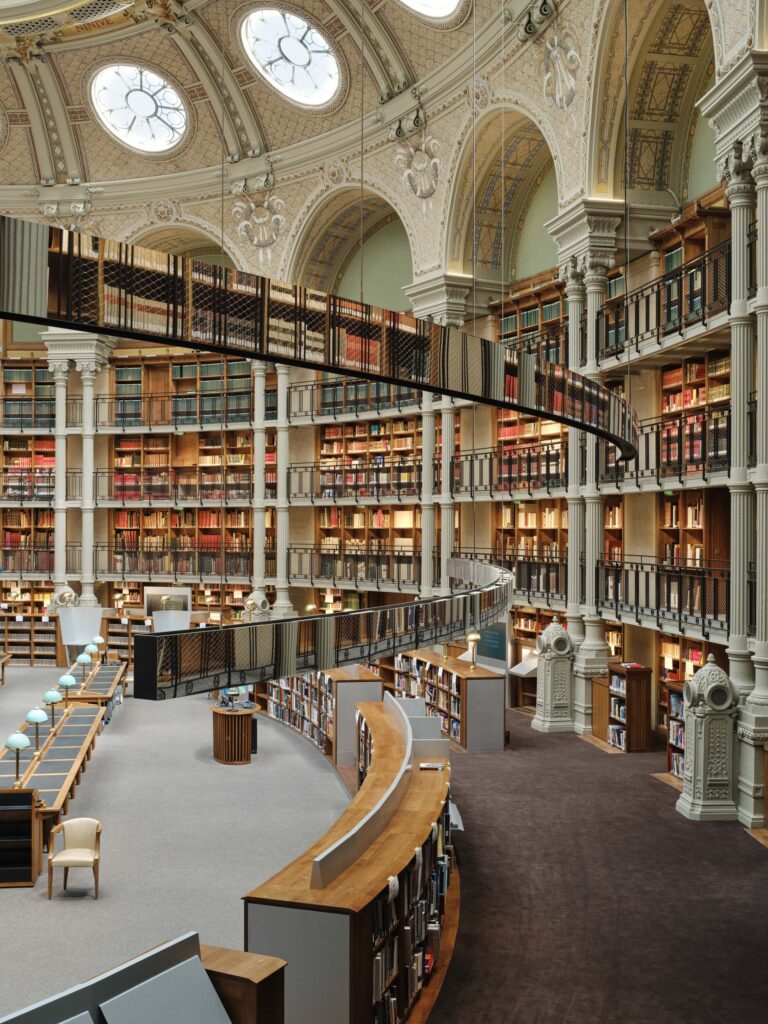

Indeed not.
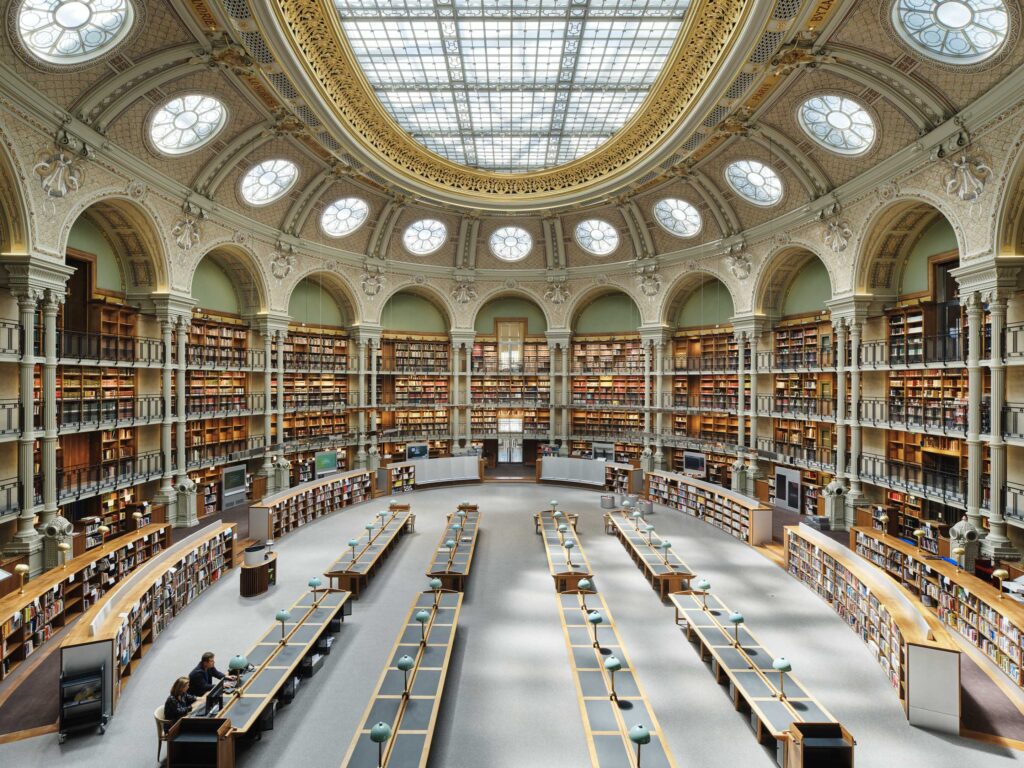
To that end, the library’s Oval Room remains a dramatic, gasp-inducing astonishment. Fully refreshed with mirrored lighting and modern shelving, this skylit space is the world’s most opulent vault.
That the space itself was built over four decades is not surprising when one reads the room: soaring slender columns, ornately detailed arches, and stacks spanning four stories. It’s a showpiece, rightly hyped as the “Oval Paradise” and clearing that impossibly high bar with aplomb. Above it all, the Oval’s dramatic glass dome showers the space in an almost ecclesiastical glow apropos of Paris’ literary pilgrims.

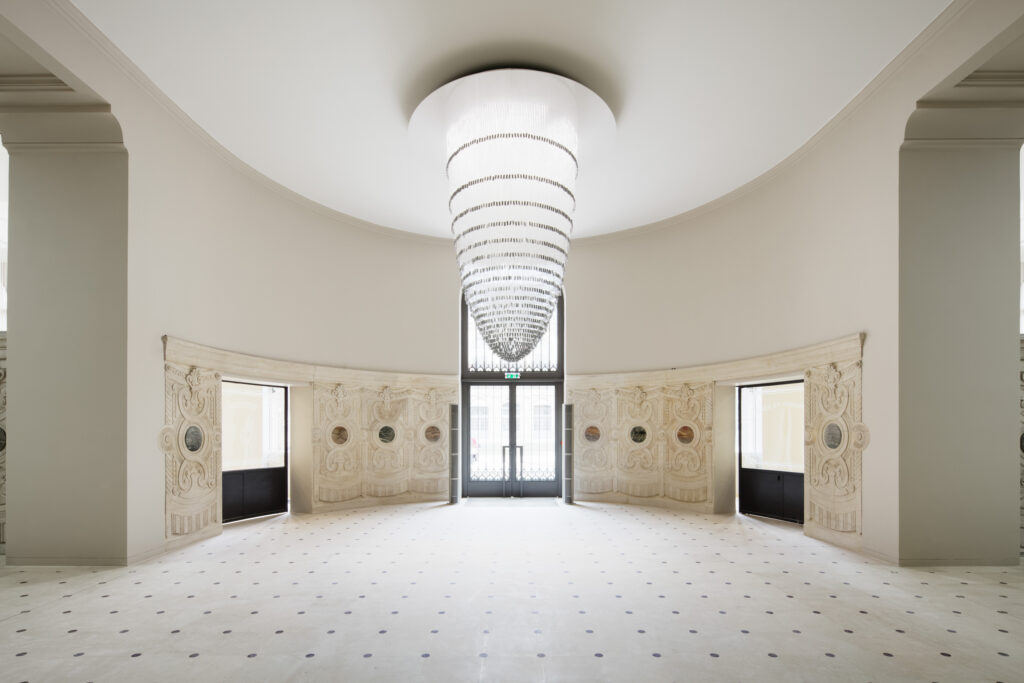
Any contemporary interpretation of Beaux-Arts decadence needs balance to lighten the opulent load. Here it is glass, used liberally.
The first “desire for connection and transparency,” the practice points out, “comes on the ground floor,” at the entrance on the rue Vivienne. “It is expressed in the façade by the transformation of three existing windows into high doors opening onto the garden.”
And it continues with new light-amplifying circulations and, in a dazzling example, a glazed conduit linking the library to an adjacent museum. Throughout is a sense of openness and expanse that guided this ship first to sea, then to shore.
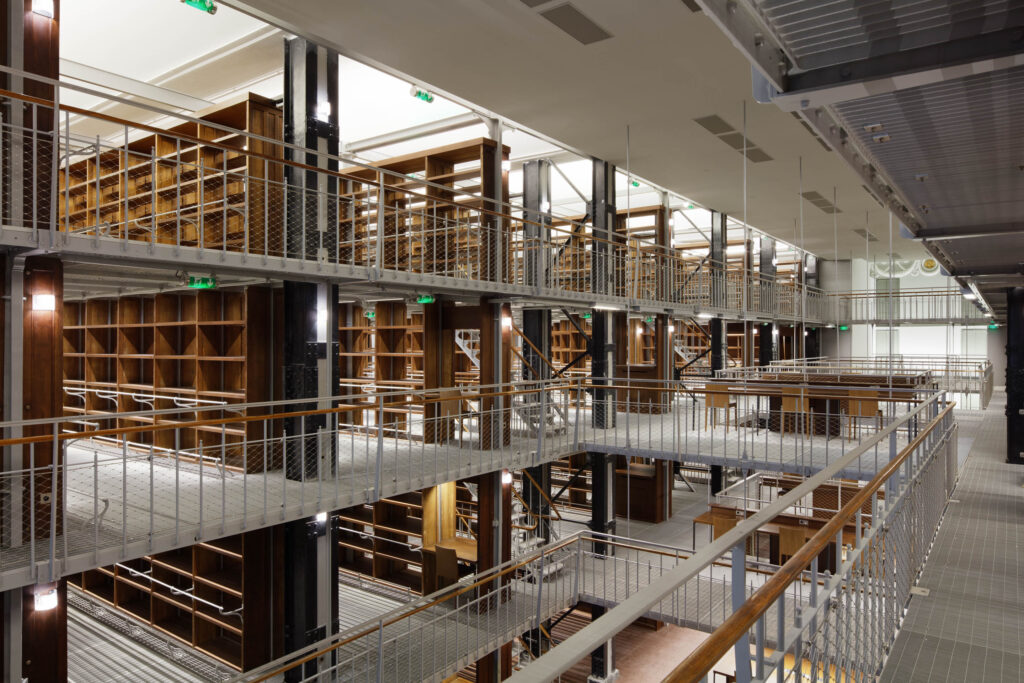



Based on a program resulting from a painstaking research process involving studies, discovery, and manpower to bring order and coherence to a set of randomly organized parts, Bruno Gaudin Architectes wrapped its work on the National Library of France in 2022, having liberated the building from constriction with interventions designed to give it a sparkling new chapter.
“Yesterday, closed in on itself,” the practice reflects, “the large, magnificent, worn, fragmented, dark and dilapidated treasure chest has now been given a new identity, full of light.”
A new history will be written.
Bruno Gaudin Architectes | bruno-gaudin.fr
Photography by Takuji Shimmura