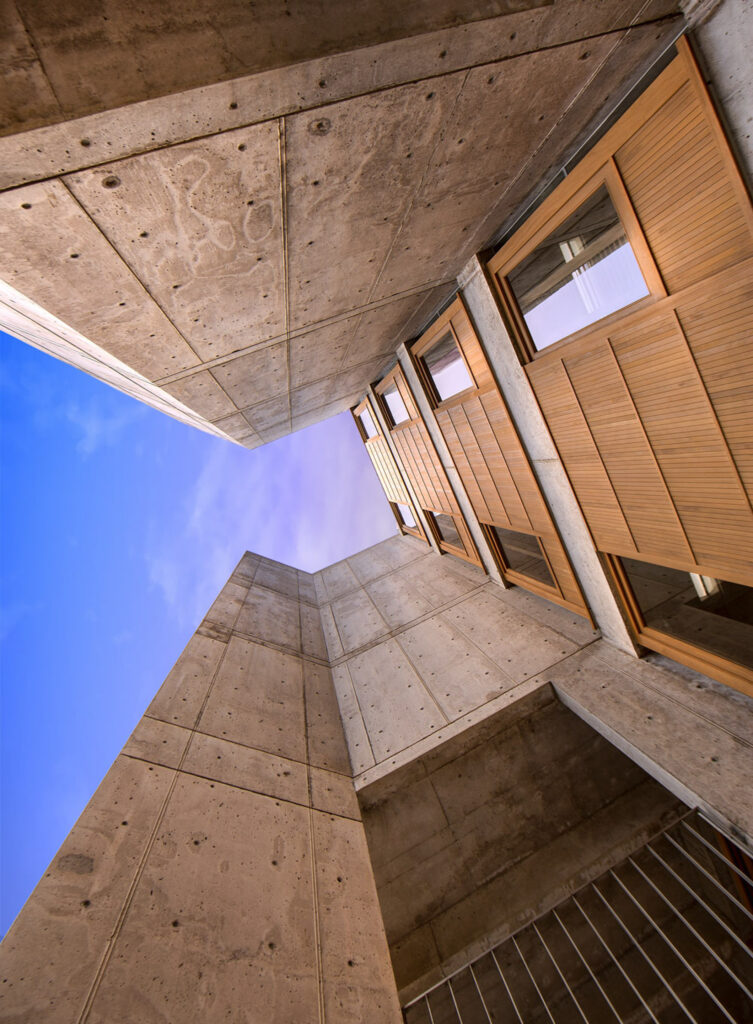
Jonas Salk founded the Salk Institute—a private, nonprofit biomedical research facility on a bluff overlooking the Pacific Coast, completed in 1965— less than a decade after he discovered the vaccine for polio, is not a surprise. He was a brilliant man. Extraordinary was Salk’s aesthetic investment, his insistence that the building created be “worthy of a visit by Picasso.”
For this, Jonas Salk needed an architect and an artist. In 20th-century icon Louis Kahn, he got both. Kahn’s vision for the project was, like all his architecture, monumental.
Practical and spiritually inspiring, with a visual characteristic that considered classical, modern and metaphysical influences, his design expresses a
Separating two symmetrical buildings is a travertine marble courtyard with a single water feature. As one enters this space from the east gate, as Jonas Salk and Louis Kahn intended, they are forced to confront the sun moving across the sky.
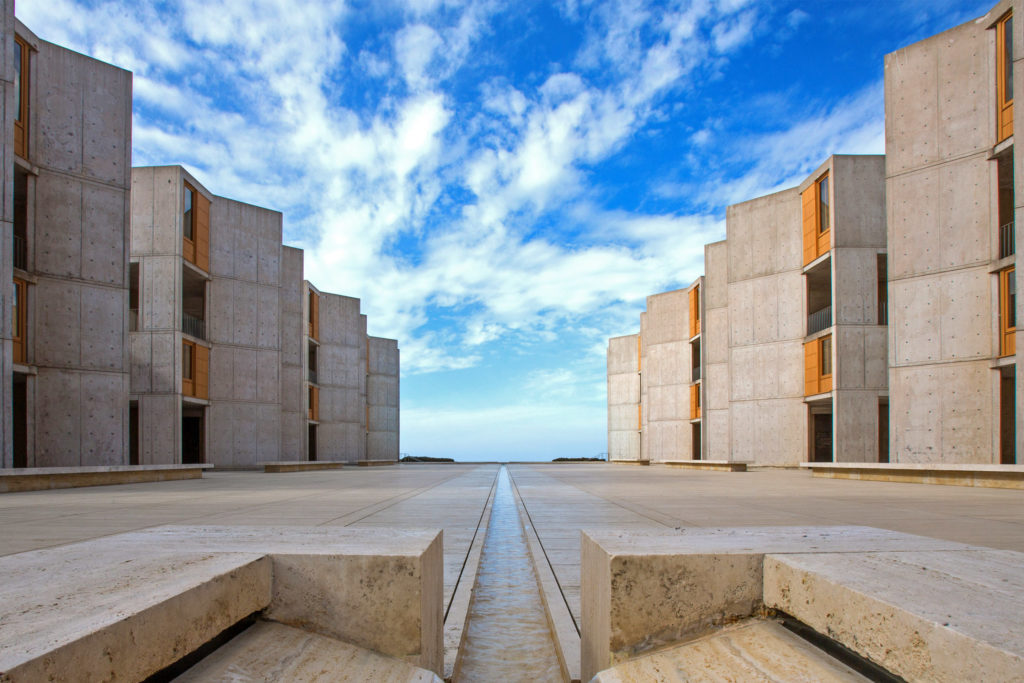

In a video produced by the Salk Institute, the complex is characterized as a “cathedral” to study, with curiosity a central tenet of scientific discovery. The courtyard might have been very different had Louis Kahn not consulted his contemporary, Mexican architect Luis Barragan, who is said to have suggested
At this suggestion, notes Salk Institute neuroscientist Tom Albright, “Jonas and Louis Kahn saw his vision and agreed.” To occupy the open space is to stand on a bridge between art and science.
“I think that was Jonas’s intent,” says Tom Albright, whose research concerns the relationship between the brain and the built environment, and knew Jonas Salk as someone deeply invested in scientific literacy.
“He was a very genuine person and someone who thought deeply between research and society,” shares Tom Albright. “That really is how he came to be a celebrity, a hero in American life; he took science and developed essentially an invention that changed the course of human civilization in the 20th century. He spent a good part of the rest part of his life stressing the fact that science is incredibly important for the way we live, and improving the way we live.”
Salk Institute is a fitting tribute to its namesake—one of the greatest buildings in the world housing one of the best biomedical research institutes in the world.
Perhaps its best endorsement is that not even a scientist can quantify the depth of what makes it special.
“I get so engrossed in my computer screen that I forget there’s this extraordinary place out there—the setting, the building itself.”
But periodically, he adds, it hits him. He could be anywhere, but he’s here.
“It’s a funny
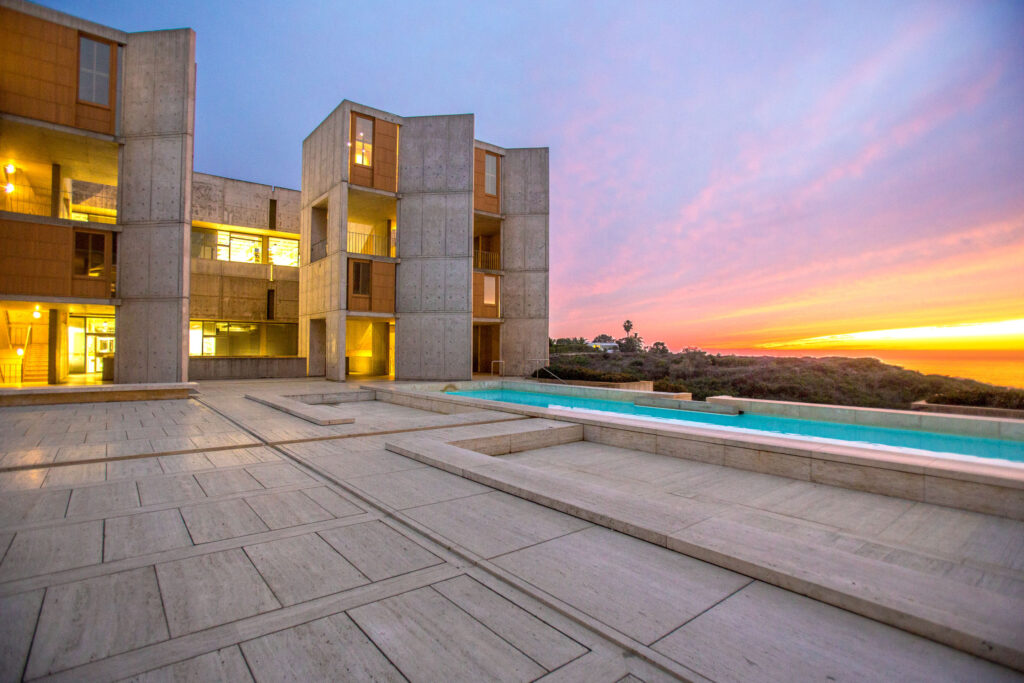

“It’s a very hard thing to characterize…but I’m absolutely convinced there’s something about what architects call
And plenty of support, with Salk Institute hosting architectural tours and trying to build a conservation endowment.
“We have a responsibility,” says Tom Albright. “We’re the curators of the Salk Institute and it’s very important for posterity that we preserve this place in this state that it’s currently in; the state intended by Louis Kahn and Jonas.
”In recent years this meant renovating the building’s weather-beaten original teak. “It was a huge financial investment for us,” admits Tom Albright, “but again, its part of our commitment to conserve the
The Salk Institute | salk.edu
Photographs: Courtesy of the Salk Institute